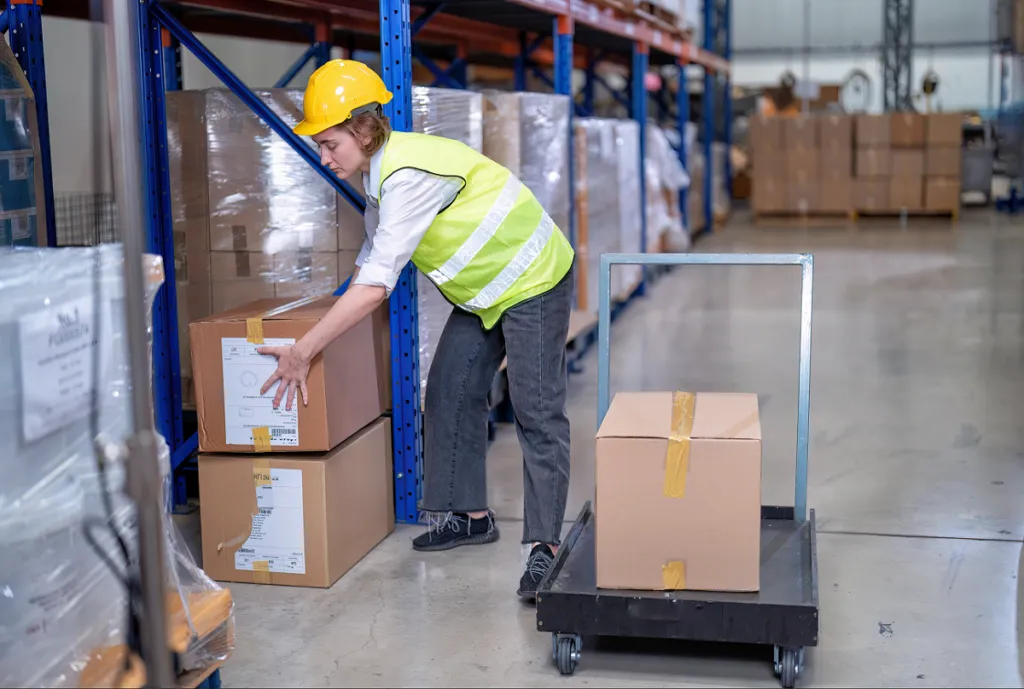
What is Manual Handling?
Manual handling involves any activity requiring an individual to lift, move, push, pull, carry or hold an object. Improper manual handling is one of the leading causes of workplace injuries, often resulting in musculoskeletal disorders such as strains, sprains and repetitive strain injuries. According to the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), manual handling injuries account for more than one-third of all workplace injuries reported each year. This article explores effective manual handling techniques and strategies to prevent workplace injuries.
Understanding Manual Handling Risks
The risks associated with manual handling can be broadly categorised into four main areas:
- The Task: Repetitive or sustained actions, strenuous pushing or pulling, and awkward postures can increase the risk of injury.
- The Load: The weight, size and shape of the object being handled can pose significant risks, especially if the load is difficult to grip or unstable.
- The Environment: Factors such as inadequate lighting, slippery floors and space constraints can contribute to accidents and injuries.
- Individual Capability: The physical fitness and health of the individual performing the task also play a crucial role. Employees with pre-existing conditions or insufficient training are more susceptible to injuries.
Effective Manual Handling Techniques
To reduce the risk of injury, it is essential to follow proper manual handling techniques. Here are some key principles:
Plan the Lift:
- Assess the Load: Check the weight and stability of the load. If it is too heavy or awkward, seek assistance or use mechanical aids.
- Clear the Path: Ensure the route to be taken is free from obstacles, well-lit and has no slip or trip hazards.
Correct Posture:
- Feet Position: Place your feet shoulder-width apart, with one foot slightly forward to maintain balance.
- Bend the Knees: Squat down by bending your knees, not your back. This allows your leg muscles to do the lifting, reducing strain on your back.
- Keep the Back Straight: Maintain a natural curve in your spine. Avoid bending or twisting your back while lifting.
Grip and Lift:
- Firm Grip: Use your whole hand to grip the load, ensuring a secure hold.
- Lift Smoothly: Lift the load smoothly and steadily, avoiding any sudden movements. Keep the load close to your body to maintain stability.
Carrying the Load:
- Keep the Load Close: Hold the load close to your waist, ensuring it does not obstruct your view.
- Use Your Feet: To change direction, move your feet instead of twisting your torso.
Lowering the Load:
- Bend the Knees: When lowering the load, bend your knees and squat down, keeping your back straight.
- Place the Load Gently: Lower the load smoothly and avoid dropping it, which can cause sudden strain.

Preventing Workplace Injuries
Beyond individual manual handling techniques, organisations can implement several strategies to prevent workplace injuries:
Training and Education:
- Regular Training: Provide regular training sessions on manual handling techniques, ensuring that all employees understand the correct methods.
- Tailored Programs: Develop training programs tailored to specific tasks and environments within the workplace.
Use of Mechanical Aids:
- Lifting Equipment: Utilise equipment such as forklifts, hoists and trolleys to handle heavy or bulky loads.
- Ergonomic Tools: Invest in ergonomic tools and devices that reduce the physical strain on employees.
Risk Assessments:
- Identify Hazards: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential manual handling hazards in the workplace.
- Implement Controls: Implement control measures to mitigate identified risks, such as redesigning workflows or providing additional support.
Ergonomic Workspaces:
- Workspace Design: Design workspaces to facilitate safe manual handling practices. This includes adequate space, proper lighting and non-slip flooring.
- Adjustable Equipment: Provide adjustable workstations and equipment to accommodate different body sizes and postures.
Health and Fitness Programs:
- Encourage Fitness: Promote physical fitness programs that enhance employees’ strength, flexibility and overall health.
- Early Intervention: Implement early intervention programs to address minor injuries before they become severe.
Manual Handling - Final Words
Manual handling is an integral part of many jobs and improper techniques can lead to serious injuries or death. By understanding the risks and implementing effective manual handling techniques and preventive measures, organisations can significantly reduce workplace injuries. Training (including online induction), ergonomic design, use of mechanical aids and a proactive approach to health and safety are essential components of a successful manual handling strategy.
Investing in these measures not only ensures the safety and well-being of employees but also enhances productivity and reduces costs associated with workplace injuries. As workplaces evolve, continuous education and adaptation of best practices in manual handling will remain crucial in creating a safe and healthy work environment.